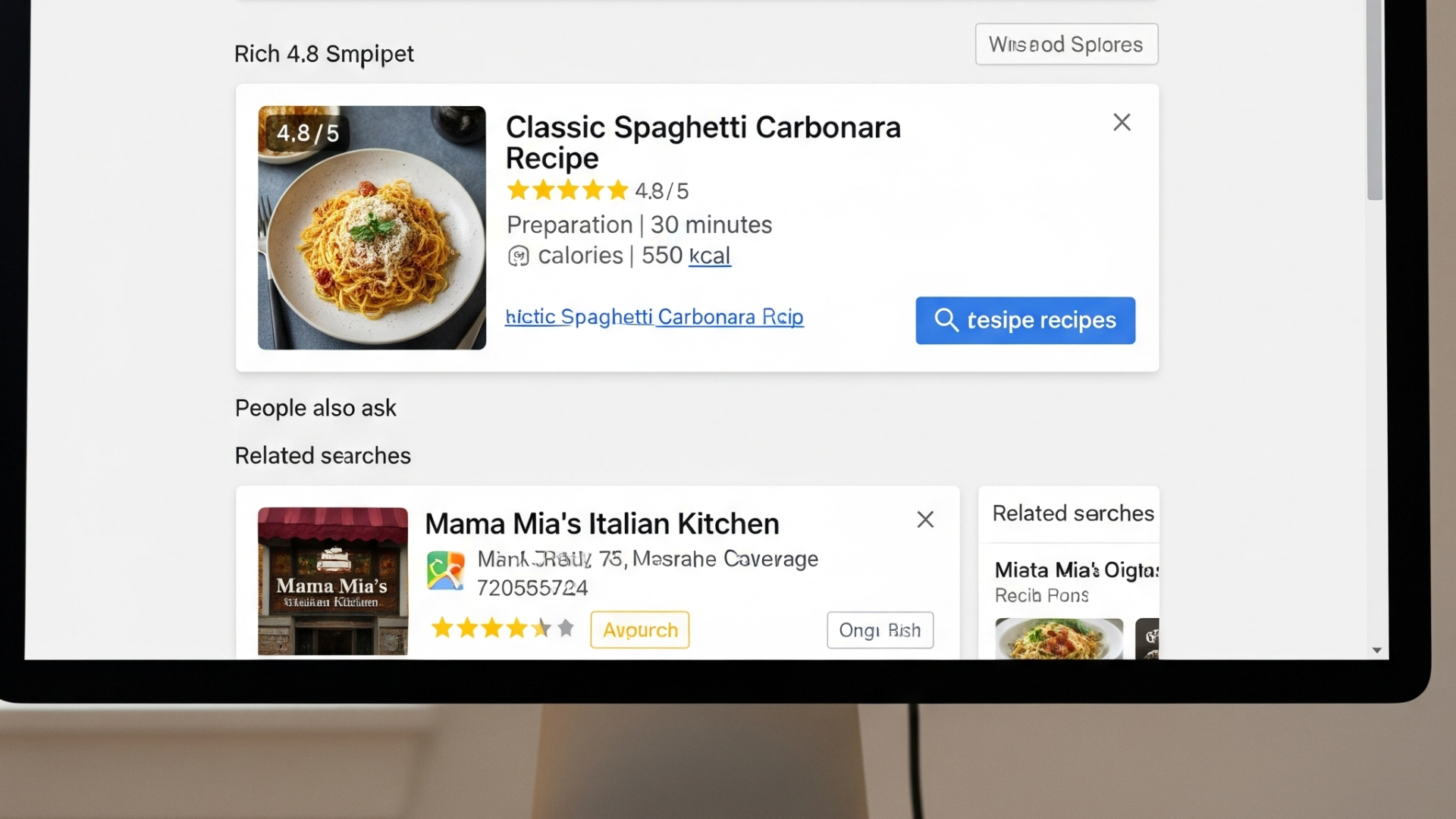
When you search for something on Google, some results stand out more than others—they may show star ratings, images, FAQs, or event details. These eye-catching enhancements are called rich snippets, and they’re powered by schema markup.
For businesses and websites aiming to grab more clicks and improve search presence, schema markup is one of the most underused yet powerful SEO tools. Let’s break it down in a beginner-friendly way.
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a type of structured data that you add to your website’s code. Think of it as a “dictionary” that explains your content to search engines in a more detailed way.
For example:
- A normal text: “Pizza House is open from 11 AM to 11 PM”
- With schema: Google knows that “Pizza House” is a business, “11 AM to 11 PM” is opening hours, and it’s a restaurant.
This added clarity helps search engines present your content more attractively in search results.
Why Does Schema Markup Matter?
- Boosts Click-Through Rates (CTR): Results with reviews, FAQs, or product details naturally attract more clicks.
- Improves Visibility: Rich snippets take more visual space on Google, pushing competitors down.
- Increases Relevance: Structured data helps Google match your page to the right search intent.
- Voice Search Ready: Schema makes it easier for voice assistants (like Alexa or Google Assistant) to pull accurate answers.

Common Types of Schema Markup
Here are some beginner-friendly schema types to start with:
- Organization Schema – Displays business details like logo, contact info, and social links.
- Local Business Schema – Perfect for local SEO, showing maps, hours, and reviews.
- Product Schema – Adds price, availability, and reviews for eCommerce sites.
- FAQ Schema – Expands your result with Q&A dropdowns.
- Article/Blog Schema – Highlights authorship, publishing date, and headline.
- Event Schema – Shows event dates, venues, and ticket info.
- Recipe Schema – Displays cooking time, calories, and ratings.
How to Implement Schema Markup
You don’t need to be a coding expert. Here are three beginner-friendly methods:
1. Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
- Visit Google’s tool.
- Paste your page URL.
- Highlight and tag elements (like name, ratings, or author).
- Copy the generated code and add it to your site.
2. Schema Plugins (For WordPress Users)
Plugins like Rank Math or Yoast SEO make schema integration simple with just a few clicks.
3. Manual JSON-LD Code
If you’re comfortable editing your website’s code, you can paste JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) directly into the <head> section.
Example for a local business:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "LocalBusiness",
"name": "Pizza House",
"image": "https://www.pizzahouse.com/logo.png",
"address": {
"@type": "PostalAddress",
"streetAddress": "123 Main Street",
"addressLocality": "Lucknow",
"addressRegion": "UP",
"postalCode": "226001",
"addressCountry": "IN"
},
"telephone": "+91-9876543210",
"openingHours": "Mo-Su 11:00-23:00"
}
</script>
Best Practices for Schema Markup
✅ Always match schema to actual content on your page.
✅ Use Google’s Rich Results Test to validate your markup.
✅ Don’t overuse schema—apply only where relevant.
✅ Keep updating your structured data as your business details change.
The Future of Search: Structured Data First
Search engines are moving towards context-driven results. Schema markup isn’t just about SEO—it’s about future-proofing your content for AI search, voice assistants, and evolving SERP features.
If you’re serious about increasing clicks, visibility, and brand authority, implementing schema markup is no longer optional—it’s essential.